p81.mw
A printed circuit board (PCB) of 100’é┤150 mm2, made of two 35 ’üŁm thin copper sheets laminated onto a 2 mm thick dielectric layer made of woven fiberglass cloth with an epoxy resin binder (FR-4), is populated by electronic chips dissipating 10 W in operation. For a thermal analysis, the board is to be assumed plugged at one of its largest edges to a rack kept at 30 ┬║C, and the dissipation distributed symmetrically between two 30 mm wide bands across the short dimension (100 mm), leaving a central band of 20 mm and two 10 mm bands at the ends. To do:
a) Make a sketch of the steady temperature field in the card.
b) Find the maximum temperature expected if only conduction heat transfer towards the plug is significant.
c) Find the temperature field taking also into account radiation heat transfer to a surrounding box at 30 ┬║C, under vacuum.
d) Find the temperature field when adding the effect of heat convection by inside air on ground with h=2 W/(m2┬ĘK).
FR-4 data:’ĆĀ’ü▓=1850 kg/m3, c=700 J/(kg┬ĘK)), k=0.25 W/(m┬ĘK)), maximum working temperature 140 ┬║C.
Data:
| > |
read"../therm_eq.m":read"../therm_proc.m":with(therm_proc):interface(rtablesize=infinity): |
| > |
su1:="FR4":su2:="Cobre":dat:=[Lx=0.1*m_,Ly=0.15*m_,Lz=2e-3*m_,Lcu=35e-6*m_,f=1,Li1=0.01*m_,Li2=0.04*m_,Li3=0.06*m_,Li4=0.09*m_,Wst=10*W_,Tb=(30+273.15)*K_,T0=(30+273.15)*K_,epsilon12=1,h12=2*W_/(m_^2*K_)]; |
Eqs. const. (F=FR-4, C=Cobre):
| > |
datF:=rho=1850*kg_/m_^3,c=700*J_/(kg_*K_),k=0.5*W_/(m_*K_),kt=0.25*W_/(m_*K_);datC:=get_sol_data(su2);dat:=op(dat),Const,SI2,SI1: |
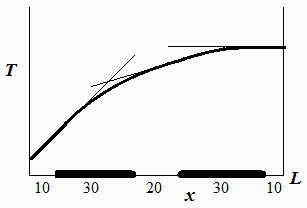
a) Make a sketch of the steady temperature field in the card.
(Fig. above). Three straight segments (where there is no dissipation), and two parabollic segments matching.to make T(x) and dT/dx continuous.
b) Find the maximum temperature expected if only conduction heat transfer towards the plug is significant.
Let Ti1, Ti2, Ti3, and Ti4 the T-values at the 4 discontinuities in phi(x). T(x) is a straight line where phi=0 and a parabola otherwise.
| > |
T01:=T0+(Ti1-T0)*x/Li1;T12:=a1+b1*x+c1*x^2;T23:=Ti2+(Ti3-Ti2)*(x-Li2)/(Li3-Li2);T34:=a2+b2*x+c2*x^2; |
We have one condition at each stright segment, plus two-each at the intermediate points (10 in total, to find the 10 unknowns: a1,b1,c1,a2,b2,c2,Ti1,Ti2,Ti3,Ti4):
| > |
eqWtotal:=Wst=k*A*(Ti1-T0)/Li1;eqWhalf:=Wst/2=k*A*(Ti3-Ti2)/(Li3-Li2);eqi1:=Ti1=subs(x=Li1,T12);eqi1_:=(Ti1-T0)/Li1=subs(x=Li1,diff(T12,x));eqi2:=Ti2=subs(x=Li2,T12);eqi2_:=(Ti3-Ti2)/(Li3-Li2)=subs(x=Li2,diff(T12,x));eqi3:=Ti3=subs(x=Li3,T34);eqi3_:=(Ti3-Ti2)/(Li3-Li2)=subs(x=Li3,diff(T34,x));eqi4:=Ti4=subs(x=Li4,T34);eqi4_:=0=subs(x=Li4,diff(T34,x));sol:=solve({eqWtotal,eqWhalf,eqi1,eqi1_,eqi2,eqi2_,eqi3,eqi3_,eqi4,eqi4_},{a1,b1,c1,a2,b2,c2,Ti1,Ti2,Ti3,Ti4}): |
With the effective conductivity, the values are:
| > |
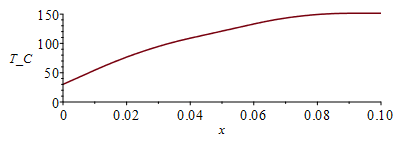
eqkeff:=k=Sum(k[i]*f[i]*delta[i],i)/Sum(delta[i],i);eqkeff:=k=(kC*f*Lcu+kF*(Lz-2*Lcu)+kC*Lcu)/(Lz+2*Lcu);eqkeff_:=k=subs(kC=k,datC,kF=k,datF,dat,rhs(%));eqA:=A=Ly*Lz;sol_:=subs(eqkeff_,eqA,dat,sol);Tmax_:=subs(sol_,Ti4);'Tmax_'=TKC(%);T_:=subs(sol_,dat,SI0,piecewise(x<=Li1,T01,(x>Li1 and x<=Li2),T12,(x>Li2 and x<=Li3),T23,(x>Li3 and x<=Li4),T34,Ti4));plot(T_-273,x=0..0.1,T_C=0..150); |
i.e. the analytical maximum temperature is 151 ┬║C.
Distribution of heat sources for 1D-model.
| > |
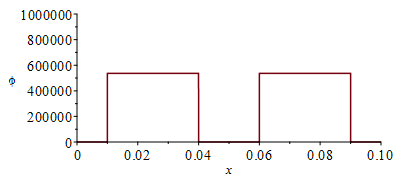
eqphim:=phim=Wst/(2*(Li2-Li1)*Ly*(Lz+2*Lcu));eqphim_:=subs(dat,SI0,%);phi0_:=subs(dat,SI0,piecewise(x<=Li1,0,(x>Li1 and x<=Li2),1,(x>Li2 and x<=Li3),0,(x>Li3 and x<=Li4),1,0)*rhs(eqphim_));plot(%,x=0..0.1,phi=0..1e6); |
c) Find the temperature field taking also into account radiation heat transfer to a surrounding box at 30 ┬║C, under vacuum.
There is no analytical solution now, and we must recourde to numerical simulation. We assume epsilon=1 (the procedure should be checked against the analytical solution when epsilon=0).
| > |
eq11_24_0_;eq11_24_gen_;T:='T':eqp:=p=2*Ly;eqeps:=epsilon[lat]=epsilon_;eqh:=h[lat]=h_;eq0:=subs(eqp,eqeps,E0=0,h0=0,eqh,epsilon0=0,eq11_24_0_);eqi:=subs(eqp,eqeps,E0=0,h0=0,eqh,epsilon0=0,eq11_24_gen_);eqN:=T[N,j+1]=T[N-1,j]; |
| > |
T:='T':N:=25;M:=3000;tsim:=2000;T0_:=subs(dat,SI0,T0);Tb_:=subs(dat,SI0,Tb);Dx:=subs(dat,SI0,Lx)/N;Dt:=tsim/M;h_:=0*subs(dat,SI0,h12);epsilon_:=subs(dat,SI0,epsilon12);sigma_:=subs(Const,SI0,sigma);Ly_:=subs(dat,SI0,Ly);Lz_:=subs(dat,SI0,Lz);p_:=2*Ly_;rho_eff:=(rhoF*Lz+2*rhoC*Lcu)/(Lz+2*Lcu);rho_:=subs(rhoF=rho,datF,rhoC=rho,datC,dat,SI0,%);c_eff:=(rhoF*cF*Lz+2*rhoC*cC*Lcu)/(rhoF*Lz+2*rhoC*Lcu);c_:=subs(cF=c,rhoF=rho,datF,cC=c,rhoC=rho,datC,dat,SI0,%);k_:=subs(SI0,rhs(eqkeff_));eqFo:=Fo='k*Dt/(rho*c*Dx^2)';Fo:=subs(k=k_,rho=rho_,c=c_,rhs(eqFo)); |
| > |
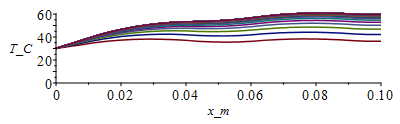
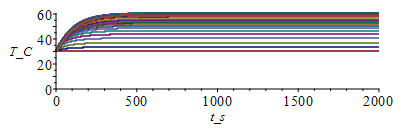
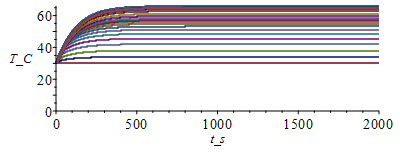
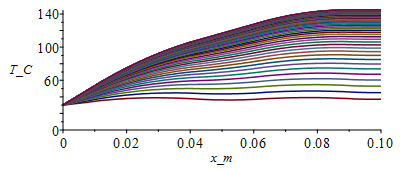
T:=Matrix(1..M,1..N+1,Tb_):for j from 1 to M-1 do T[j+1,1]:=Tb_;for i from 2 to N do phi_:=evalf(subs(x=(i-1)*Dx,phi0_));T[j+1,i]:=T[j,i]+Fo*(T[j,i-1]-2*T[j,i]+T[j,i+1])+phi_*Dt/(rho_*c_)-(p_*Dt/(rho_*c_*Lz_*Ly_))*(h_*(T[j,i]-T0_)+epsilon_*sigma_*(T[j,i]^4-T0_^4));od: T[j+1,N+1]:=T[j+1,N];od:Tmax:=max(T)*K_;'Tmax'=TKC(%);i:='i':j:='j':sx:=seq([seq([i*Dx-Dx,T[j*50,i]-273],i=1..N+1)],j=1..M/50):plot([sx],x_m=0..0.1,T_C=0..(Tmax/K_)-273);st:=seq([seq([j*Dt,T[j,i]-273],j=1..M)],i=1..N+1):plot([st],t_s=0..tsim,T_C=0..(Tmax/K_)-273); |
Notice that there is dT/dx<0 at the steady state now, because some heat goes by conduction towards the adiabatic edge, to be evacuated by radiation.
Check for epsilo=0
| > |
T:='T':eq11_24_0_;eq11_24_gen_;eqp:=p=2*Ly;eqeps:=epsilon[lat]=epsilon_;eqh:=h[lat]=h_;eq0:=subs(eqp,eqeps,E0=0,h0=0,eqh,epsilon0=0,eq11_24_0_);eqi:=subs(eqp,eqeps,E0=0,h0=0,eqh,epsilon0=0,eq11_24_gen_);eqN:=T[N,j+1]=T[N-1,j];T:='T':N:=25;M:=3000;tsim:=2000;T0_:=subs(dat,SI0,T0);Tb_:=subs(dat,SI0,Tb);Dx:=subs(dat,SI0,Lx)/N;Dt:=tsim/M;h_:=0*subs(dat,SI0,h12);epsilon_:=0*subs(dat,SI0,epsilon12);sigma_:=subs(Const,SI0,sigma);Ly_:=subs(dat,SI0,Ly);Lz_:=subs(dat,SI0,Lz);p_:=2*Ly_;rho_eff:=(rhoF*Lz+2*rhoC*Lcu)/(Lz+2*Lcu);rho_:=subs(rhoF=rho,datF,rhoC=rho,datC,dat,SI0,%);c_eff:=(rhoF*cF*Lz+2*rhoC*cC*Lcu)/(rhoF*Lz+2*rhoC*Lcu);c_:=subs(cF=c,rhoF=rho,datF,cC=c,rhoC=rho,datC,dat,SI0,%);k_:=subs(SI0,rhs(eqkeff_));eqFo:=Fo='k*Dt/(rho*c*Dx^2)';Fo:=subs(k=k_,rho=rho_,c=c_,rhs(eqFo));T:=Matrix(1..M,1..N+1,Tb_):for j from 1 to M-1 do T[j+1,1]:=Tb_;for i from 2 to N do phi_:=evalf(subs(x=(i-1)*Dx,phi0_));T[j+1,i]:=T[j,i]+Fo*(T[j,i-1]-2*T[j,i]+T[j,i+1])+phi_*Dt/(rho_*c_)-(p_*Dt/(rho_*c_*Lz_*Ly_))*(h_*(T[j,i]-T0_)+epsilon_*sigma_*(T[j,i]^4-T0_^4));od: T[j+1,N+1]:=T[j+1,N];od:Tmax:=max(T)*K_;'Tmax'=TKC(%);i:='i':j:='j':sx:=seq([seq([i*Dx-Dx,T[j*50,i]-273],i=1..N+1)],j=1..M/50):plot([sx],x_m=0..0.1,T_C=0..(Tmax/K_)-273);st:=seq([seq([j*Dt,T[j,i]-273],j=1..M)],i=1..N+1):plot([st],t_s=0..tsim,T_C=0..(Tmax/K_)-273); |
well, not too far (tmax=145 ┬║C) from the theoretical limit (Tmax=152 ┬║C).
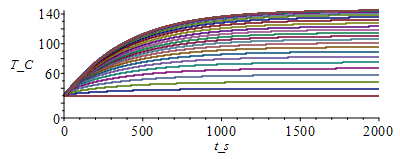
d) Find the temperature field when adding the effect of heat convection by inside air on ground with h=2 W/(m2┬ĘK).
| > |
T:='T':eq11_24_0_;eq11_24_gen_;eqp:=p=2*Ly;eqeps:=epsilon[lat]=epsilon_;eqh:=h[lat]=h_;eq0:=subs(eqp,eqeps,E0=0,h0=0,eqh,epsilon0=0,eq11_24_0_);eqi:=subs(eqp,eqeps,E0=0,h0=0,eqh,epsilon0=0,eq11_24_gen_);eqN:=T[N,j+1]=T[N-1,j];T:='T':N:=25;M:=3000;tsim:=2000;T0_:=subs(dat,SI0,T0);Tb_:=subs(dat,SI0,Tb);Dx:=subs(dat,SI0,Lx)/N;Dt:=tsim/M;h_:=subs(dat,SI0,h12);epsilon_:=subs(dat,SI0,epsilon12);sigma_:=subs(Const,SI0,sigma);Ly_:=subs(dat,SI0,Ly);Lz_:=subs(dat,SI0,Lz);p_:=2*Ly_;rho_eff:=(rhoF*Lz+2*rhoC*Lcu)/(Lz+2*Lcu);rho_:=subs(rhoF=rho,datF,rhoC=rho,datC,dat,SI0,%);c_eff:=(rhoF*cF*Lz+2*rhoC*cC*Lcu)/(rhoF*Lz+2*rhoC*Lcu);c_:=subs(cF=c,rhoF=rho,datF,cC=c,rhoC=rho,datC,dat,SI0,%);k_:=subs(SI0,rhs(eqkeff_));eqFo:=Fo='k*Dt/(rho*c*Dx^2)';Fo:=subs(k=k_,rho=rho_,c=c_,rhs(eqFo));T:=Matrix(1..M,1..N+1,Tb_):for j from 1 to M-1 do T[j+1,1]:=Tb_;for i from 2 to N do phi_:=evalf(subs(x=(i-1)*Dx,phi0_));T[j+1,i]:=T[j,i]+Fo*(T[j,i-1]-2*T[j,i]+T[j,i+1])+phi_*Dt/(rho_*c_)-(p_*Dt/(rho_*c_*Lz_*Ly_))*(h_*(T[j,i]-T0_)+epsilon_*sigma_*(T[j,i]^4-T0_^4));od: T[j+1,N+1]:=T[j+1,N];od:Tmax:=max(T)*K_;'Tmax'=TKC(%);i:='i':j:='j':sx:=seq([seq([i*Dx-Dx,T[j*50,i]-273],i=1..N+1)],j=1..M/50):plot([sx],x_m=0..0.1,T_C=0..(Tmax/K_)-273);st:=seq([seq([j*Dt,T[j,i]-273],j=1..M)],i=1..N+1):plot([st],t_s=0..tsim,T_C=0..(Tmax/K_)-273); |
as expected, Tmax=61 ┬║C with h=2 W/(m2┬ĘK) and epsilon=1, is below Tmax=66 ┬║C with h=0 and epsilon=1, and much lower than Tmax=145 ┬║C with h=epsilon=0.

![eqkeff := k = `/`(`*`(Sum(`*`(k[i], `*`(f[i], `*`(delta[i]))), i)), `*`(Sum(delta[i], i)))](images/p811_20.gif)

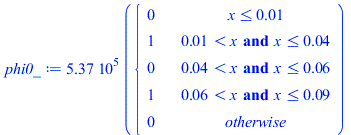
![T[i, `+`(j, 1)] = `+`(T[i, j], `*`(Fo, `*`(`+`(T[`+`(i, 1), j], `-`(`*`(2, `*`(T[i, j]))), T[`+`(i, `-`(1)), j]))), `/`(`*`(phi, `*`(Dt)), `*`(rho, `*`(c))), `-`(`/`(`*`(p, `*`(Dt, `*`(`+`(`*`(h[lat],...](images/p811_35.gif)

![T[i, `+`(j, 1)] = `+`(`*`(.1624732972, `*`(T[i, j])), `*`(.4187633514, `*`(T[`+`(i, 1), j])), `*`(.4187633514, `*`(T[`+`(i, `-`(1)), j])), `/`(`*`(`/`(2, 3), `*`(phi)), `*`(rho, `*`(c))), `-`(`/`(`*`(...](images/p811_67.gif)
![T[i, `+`(j, 1)] = `+`(`*`(.1624732972, `*`(T[i, j])), `*`(.4187633514, `*`(T[`+`(i, 1), j])), `*`(.4187633514, `*`(T[`+`(i, `-`(1)), j])), `/`(`*`(`/`(2, 3), `*`(phi)), `*`(rho, `*`(c))), `-`(`/`(`*`(...](images/p811_99.gif)