| > | restart:#"m13_p38" |
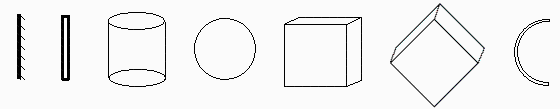
Find the steady temperature at 1 AU, for an isothermal blackbody with the following geometries: planar one-side surface (i.e. rear insulated), plate, cylinder, sphere, and cubic box in its three symmetric orientations
Datos:
| > | read`../therm_eq.m`:read`../therm_const.m`:read`../therm_proc.m`:with(therm_proc): |
| > | dat:=[E=1370*W_/m_^2]; |
| > | dat:=op(dat),Const,SI2,SI1: |
a) Find the steady temperature at 1 AU, for an isothermal blackbody with the following geometries:
Energy balance, and steady state temperature for a blackbody:
| > | eqEB:=alpha*Afrontal*E=epsilon*Aext*sigma*Tst^4;Tst:=(Afrontal*E/(Aext*sigma))^(1/4); |
Planar one side.
For one-side planar surface of area A with its normal tilted an angle beta to Sun rays, frontal area Af=Acos’üó, and emitting area Ae=A, thence
| > | Afrontal:=A*cos(beta);Aext:=A;Tst_:=Tst;Tst0_:=evalf(subs(beta=0,dat,SI0,%))*K_;'Tst0_'=TKC(%); |
Planar two sides.
For a plate emitting from both sides,
| > | Afrontal:=A*cos(beta);Aext:=2*A;Tst_:=Tst;Tst0_:=evalf(subs(beta=0,dat,SI0,%))*K_;'Tst0_'=TKC(%); |
Cylinder.
For a cylinder of diameter D and length L with its axis tilted an angle beta to Sun rays, with all its surfaces emitting.
| > | Afrontal:=(Pi*D^2/4)*cos(beta)+Pi*D*L*sin(beta)/2;Aext:=2*(Pi*D^2/4)+Pi*D*L;Tst_:=Tst;Tst0_DL:=evalf(subs(beta=0,L=D,dat,SI0,%))*K_;'Tst0_'=TKC(%);Tst90_DL:=evalf(subs(beta=Pi/2,L=D,dat,SI0,Tst_))*K_;'Tst90_'=TKC(%); |
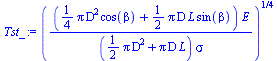 |
Sphere.
| > | Afrontal:=Pi*D^2/4;Aext:=Pi*D^2;Tst_:=Tst;Tst0_:=evalf(subs(beta=0,dat,SI0,%))*K_;'Tst0_'=TKC(%); |
Cube. Frontal.
For a frontal cube, i.e. an hexahedron of face area A, with all its surfaces emitting, Af=A and Ae=6A, thence:
| > | Afrontal:=A;Aext:=6*A;Tst_:=Tst;Tst0_:=evalf(subs(beta=0,dat,SI0,%))*K_;'Tst0_'=TKC(%); |
Cube at 45┬║.
For a cube tilted 45┬║, i.e. an hexahedron with two opposite edges and the Sun in the same plane, Af=sqrt(2)*A, and Ae=6A, thence:
| > | Afrontal:=A*sqrt(2);Aext:=6*A;Tst_:=Tst;Tst0_:=evalf(subs(beta=0,dat,SI0,%))*K_;'Tst0_'=TKC(%); |
Cube point-to-point.
For a cube pointing to the Sun, i.e. an hexahedron with two opposite vertices and the Sun in the same straight line (3 lit faces tilted 54.7┬║, instead of 2 lit faces tilted 45┬║ in the previous case),Af=sqrt(3)*A and Ae=6A, thence:
| > | Afrontal:=A*sqrt(3);Aext:=6*A;Tst_:=Tst;Tst0_:=evalf(subs(beta=0,dat,SI0,%))*K_;'Tst0_'=TKC(%); |
Notice that only fully-convex surfaces have been considered; otherwise, view factors enter into play. For instance, consider a hemispherical shell with its symmetry axis aligned with the Sun.
Afrontal:=Pi*D^2/4;Aext:=Pi*D^2;eqEB:=alpha*Afrontal*E=epsilon*(F[1,ext]*A[1,ext]+F[1,int]*A[1,int])*sigma*Tst^4;F[1,ext]:=1;F[1,int]:=1/2;A[1,ext]:=Pi*D^2/2;A[1,int]:=Pi*D^2/2;Tst:=(Afrontal*E/((F[1,ext]*A[1,ext]+F[1,int]*A[1,int])*sigma))^(1/4);Tst_:=evalf(subs(dat,SI0,%))*K_;'Tst_'=TKC(%);
Notice that a hollow hemisphere gets warmer than a spherical shell, having the same frontal area and exposed area, at 26 ┬║C instead of at 6 ┬║C, because the concave part re-radiates to itself.
| > |